Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator would like to change the private IP address of the NAT VM I72.l6.101.il to a public address of 80.80.80.1 as the packets leave the NAT-Segment network.
Which type of NAT solution should be implemented to achieve this?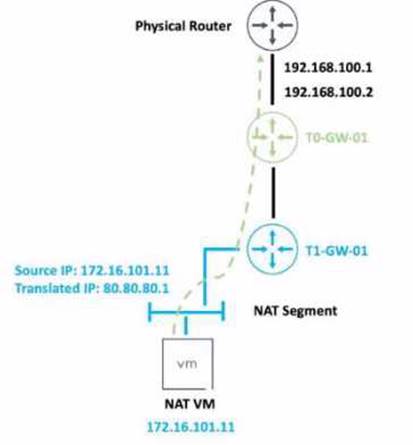
Correct Answer:
B
SNAT stands for Source Network Address Translation. It is a type of NAT that translates the source IP address of outgoing packets from a private address to a public address. SNAT is used to allow hosts in a private network to access the internet or other public networks1
In the exhibit, the administrator wants to change the private IP address of the NAT VM 172.16.101.11 to a public address of 80.80.80.1 as the packets leave the NAT-Segment network. This is an example of SNAT, as the source IP address is modified before the packets are sent to an external network.
According to the VMware NSX 4.x Professional Exam Guide, SNAT is one of the topics covered in the exam objectives2
To learn more about SNAT and how to configure it in VMware NSX, you can refer to the following resources:  VMware NSX Documentation: NAT 3
VMware NSX Documentation: NAT 3 VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NAT Configuration 4
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NAT Configuration 4  VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NAT Troubleshooting 5
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NAT Troubleshooting 5
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-7AD2C384-4303-4D6C-A
What are the four types of role-based access control (RBAC) permissions? (Choose four.)
Correct Answer:
ABDF
The four types of role-based access control (RBAC) permissions are Read, None, Full access, and Execu Read permission allows the user to view the configuration and status of the system. None permission denies any access to the system. Full access permission grants all permissions including Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD). Execute permission includes Read and Update permissions1. Auditor, Enterprise Admin, and Network Admin are not types of permissions, but types of roles that have different sets of permissions. References: NSX Features
There are four types of permissions. Included in the list are the abbreviations for the permissions that are used in the Roles and Permissions and Roles and Permissions for Manager Mode tables. Full access (FA) - All permissions including Create, Read, Update, and Delete
Full access (FA) - All permissions including Create, Read, Update, and Delete  Execute (E) - Includes Read and Update
Execute (E) - Includes Read and Update Read (R)
Read (R)  None
None
NSX-T Data Center has the following built-in roles. Role names in the UI can be different in the API.
In NSX-T Data Center, if you have permission, you can clone an existing role, add a new role, edit newly created roles, or delete newly created roles.
Role-Based Access Control (vmware.com)
What must be configured on Transport Nodes for encapsulation and decapsulation of Geneve protocol?
Correct Answer:
D
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, TEP stands for Tunnel End Point and is a logical interface that must be configured on transport nodes for encapsulation and decapsulation of Geneve protocol. Geneve is a tunneling protocol that encapsulates the original packet with an outer header that contains metadata such as the virtual network identifier (VNI) and the transport node IP address. TEPs are responsible for adding and removing the Geneve header as the packet traverses the overlay network.
Which two statements are correct about East-West Malware Prevention? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AE
East-West Malware Prevention is a feature of NSX Advanced Threat Prevention that can detect and prevent malicious files in the network traffic between virtual machines (east-west) and between the data center and the external network (north-south). To enable this feature, a Service Virtual Machine (SVM) is deployed on every ESXi host to intercept and analyze the files in the east-west traffic. An agent must also be installed on every NSX Edge node to intercept and analyze the files in the north-south traffic. The NSX Application Platform is a cloud-based service that provides threat intelligence and analysis for the NSX Malware Prevention feature. The NSX Application Platform must have Internet access to receive updates and send files for analysis. The NSX Edge nodes must also have Internet access to communicate with the NSX Application Platform.
References: Overview of NSX IDS/IPS and NSX Malware Prevention
Overview of NSX IDS/IPS and NSX Malware Prevention  Administering NSX Malware Prevention
Administering NSX Malware Prevention
Which two built-in VMware tools will help Identify the cause of packet loss on VLAN Segments? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
BE
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, Packet Capture and Traceflow are two built-in VMware tools that can help identify the cause of packet loss on VLAN segments.
Packet Capture allows you to capture packets on a specific interface or segment and analyze them using tools such as Wireshark or tcpdump. Packet Capture can help you diagnose network issues such as misconfigured MTU, incorrect VLAN tags, or firewall drops.
Traceflow allows you to inject synthetic packets into the network and trace their path from source to destination. Traceflow can help you verify connectivity, routing, and firewall rules between virtual machines or segments. Traceflow can also show you where packets are dropped or modified along the way.