Which two statements regarding FortiAnalyzer log forwarding modes are true? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AD
Both modes, forwarding and aggregation, support encryption of logs between devices.
Both forwarding and aggregation modes can use encryption to securely transfer logs between FortiAnalyzer devices.
Aggregation mode stores logs and content files and uploads them to another FortiAnalyzer device at a scheduled time.
In aggregation mode, logs are stored and then transferred to another FortiAnalyzer at a scheduled time, rather than in real-time. This mode is typically used when consolidating logs from multiple devices into a central FortiAnalyzer.
The other options are incorrect because:
Forwarding mode sends logs in real-time but not exclusively to other FortiAnalyzer devices; it can also send logs to external systems like syslog servers.
Aggregation mode is primarily for consolidating logs to another FortiAnalyzer and doesn't focus on forwarding logs to syslog or CEF servers.
Refer to the exhibit.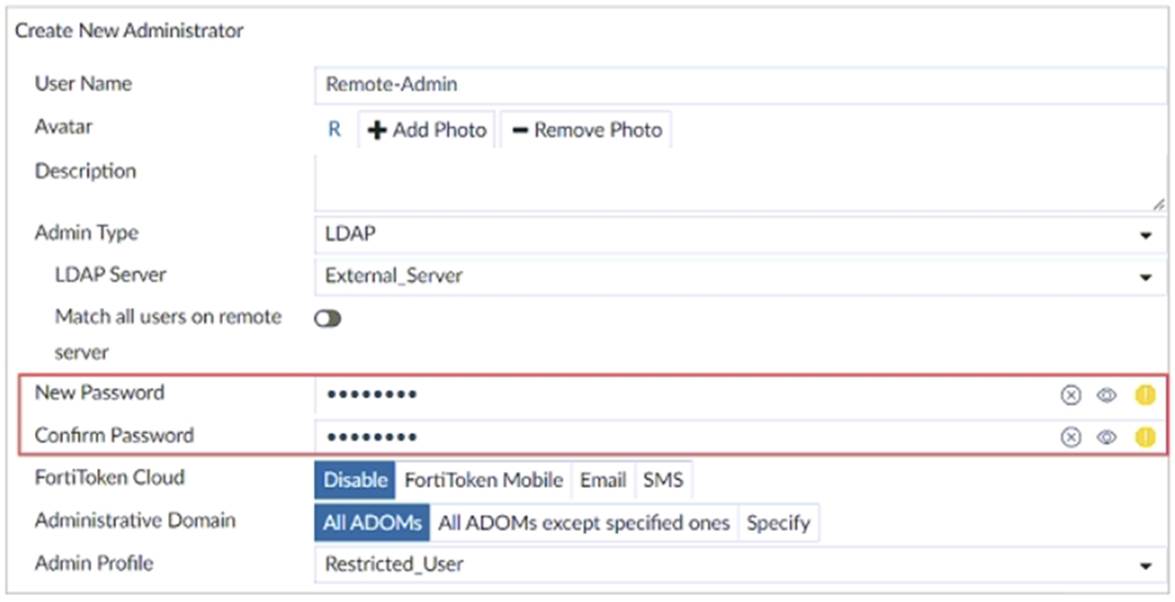
The exhibit shows the creation of a new administrator on FortiAnalyzer. The new account uses the credentials stored on an LDAP server.
Why would an administrator configure a password for this account?
Correct Answer:
A
When using LDAP for authentication, a password can be set locally on FortiAnalyzer as a fallback option in case the LDAP server becomes unreachable. This ensures that the administrator can still log in if there are issues with the LDAP server.
What FortiGate process caches logs when FortiAnalyzer is not reachable?
Correct Answer:
D
The miglogd process on FortiGate is responsible for caching logs when FortiAnalyzer is unreachable. It temporarily stores logs in memory and, if the memory buffer fills up, it starts storing logs on disk. Once the connection to FortiAnalyzer is restored, miglogd sends the cached logs to the FortiAnalyzer.
You finished registering a FortiGate device. After traffic starts to flow through FortiGate, you notice that only some of the logs expected are being received on FortiAnalyzer.
What could be the reason for the logs not arriving on FortiAnalyzer?
Correct Answer:
C
When only some of the expected logs from a FortiGate device are being received on FortiAnalyzer, it often indicates a configuration issue on the FortiGate side. Proper logging configuration on FortiGate involves specifying what types of logs to generate (e.g., traffic, event, security logs) and ensuring that these logs are directed to the FortiAnalyzer unit for storage and analysis. If the logging settings on FortiGate are not correctly configured, it could result in incomplete log data being sent to FortiAnalyzer. This might include missing logs for certain types of traffic or events that are not enabled for logging on the FortiGate device.
Ensuring comprehensive logging is enabled and correctly directed to FortiAnalyzer is crucial for full visibility into network activities and for the effective analysis and reporting of security incidents and network performance.
What does the disk status Degraded mean for RAID management?
Correct Answer:
B
When the RAID status is Degraded, it typically indicates that one or more drives in the RAID array have failed or are missing, causing the RAID array to operate with reduced redundancy. In this state, the array is still functioning, but it's at risk because the fault tolerance provided by RAID is compromised.