A digital certificate, also known as an X.509 certificate, contains which two pieces of information? (Choose two.)
Correct Answer:
AC
A digital certificate, also known as an X.509 certificate, contains two pieces of information:  Issuer, which is the identity of the certificate authority (CA) that issued the certificate
Issuer, which is the identity of the certificate authority (CA) that issued the certificate Public key, which is the public part of the asymmetric key pair that is associated with the certificate subject
Public key, which is the public part of the asymmetric key pair that is associated with the certificate subject
References:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/certificate-management
What happens when a certificate is revoked? (Choose two)
Correct Answer:
BC
When a certificate is revoked, it means that it is no longer valid and should not be trusted by any entity. Revoked certificates are automatically added to the certificate revocation list (CRL) which is published by the issuing CA and can be checked by other parties. If a CA certificate is revoked, all certificates signed by that CA are also revoked and added to the CRL. Revoked certificates can be reinstated if the reason for revocation is resolved, such as a compromised private key being recovered or a misissued certificate being corrected. External CAs do not query FortiAuthenticator for revoked certificates, but they can use protocols such as SCEP or OCSP to exchange certificate information with FortiAuthenticator. References: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4/administration-guide/372408/certificate-management
Which two protocols are the default management access protocols for administrative access for FortiAuthenticator? (Choose two)
Correct Answer:
BC
HTTPS and SSH are the default management access protocols for administrative access for FortiAuthenticator. HTTPS allows administrators to access the web-based GUI of FortiAuthenticator using a web browser and a secure connection. SSH allows administrators to access the CLI of FortiAuthenticator using an SSH client and an encrypted connection. Both protocols require the administrator to enter a valid username and password to log in.
References:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/system-settings#manag
A device or user identity cannot be established transparently, such as with non-domain BYOD devices, and allow users to create their own credentialis.
In this case, which user idendity discovery method can Fortiauthenticator use?
Correct Answer:
D
Portal authentication is a user identity discovery method that can be used when a device or user identity cannot be established transparently, such as with non-domain BYOD devices, and allow users to create their own credentials. Portal authentication requires users to enter their credentials on a web page before accessing network resources. The other methods are used for transparent identification of domain devices or users. References:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4/administration-guide/372406/user-identity-discovery
Examine the screenshot shown in the exhibit.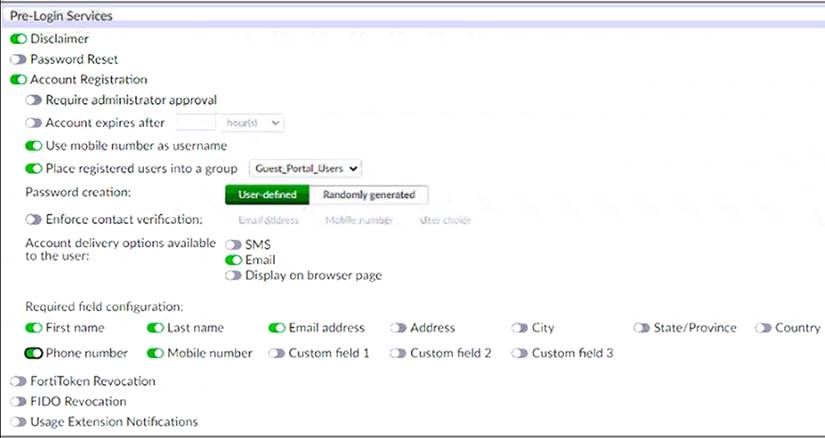
When generating a TOTP for two-factor authentication, what two pieces of information are used by the algorithm to generate the TOTP?
Correct Answer:
B
TOTP stands for Time-based One-time Password, which is a type of OTP that is generated based on two
pieces of information: time and seed. The time is the current timestamp that is synchronized between the client and the server. The seed is a secret key that is shared between the client and the server. The TOTP algorithm combines the time and the seed to generate a unique and short-lived OTP that can be used for two-factor authentication.
References:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/two-factor-authenticati