What is the expected output of the following code?
Correct Answer:
C
The code snippet that you have sent is a conditional statement that checks if a variable ??counter?? is less than 0, greater than or equal to 42, or neither. The code is as follows: if counter < 0: print(????) elif counter >= 42: print(????) else: print(????)
The code starts with checking if the value of ??counter?? is less than 0. If yes, it prints a single asterisk () to the screen and exits the statement. If no, it checks if the value of ??counter?? is greater than or equal to 42. If yes, it prints three asterisks () to the screen and exits the statement. If no, it prints two asterisks () to the screen and exits the statement.
The expected output of the code depends on the value of ??counter??. If the value of ??counter?? is 10, as shown in the image, the code will print two asterisks (**) to the screen, because 10 is neither less than 0 nor greater than or equal to 42. Therefore, the correct answer is C.
* *
Reference: [Python Institute - Entry-Level Python Programmer Certification]
What is the expected result of running the following code?
Correct Answer:
C
The code snippet that you have sent is trying to use the index method to find the position of a value in a list. The code is as follows:
the_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(the_list.index(6))
The code starts with creating a list called ??the_list?? that contains the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. Then, it tries to print the result of calling the index method on the list with the argument 6. The index method is used to return the first occurrence of a value in a list. For example, the_list.index(1) returns 0, because 1 is the first value in the list.
However, the code has a problem. The problem is that the value 6 is not present in the list, so the index method cannot find it. This will cause a ValueError exception, which is an error that occurs when a function or operation receives an argument that has the right type but an inappropriate value. The code does not handle the exception, and therefore it will terminate with an error message.
The expected result of the code is an unhandled exception, because the code tries to find a value that does not exist in the list. Therefore, the correct answer is C. The code raises an unhandled exception.
Reference: Python List index() Method - W3SchoolsPython Exceptions: An Introduction –
Real Python
What is the expected output of the following code?
Correct Answer:
C
The code snippet that you have sent is checking if two numbers are equal and printing the result. The code is as follows:
num1 = 1 num2 = 2 if num1 == num2: print(4) else: print(1)
The code starts with assigning the values 1 and 2 to the variables ??num1?? and ??num2?? respectively. Then, it enters an if statement that compares the values of ??num1?? and ??num2?? using the equality operator (==). If the values are equal, the code prints 4 to the screen. If the values are not equal, the code prints 1 to the screen.
The expected output of the code is 1, because the values of ??num1?? and ??num2?? are not equal. Therefore, the correct answer is C. 1.
Reference: [Python Institute - Entry-Level Python Programmer Certification]
What is true about tuples? (Select two answers.)
Correct Answer:
AD
Tuples are one of the built-in data types in Python that are used to store collections of data. Tuples have some characteristics that distinguish them from other data types, such as lists, sets, and dictionaries. Some of these characteristics are:
✑ Tuples are immutable, which means that their contents cannot be changed during their lifetime. Once a tuple is created, it cannot be modified, added, or removed. This makes tuples more stable and reliable than mutable data types. However, this also means that tuples are less flexible and dynamic than mutable data types. For example, if you want to change an element in a tuple, you have to create a new tuple with the modified element and assign it to the same variable12
✑ Tuples are ordered, which means that the items in a tuple have a defined order and can be accessed by using their index. The index of a tuple starts from 0 for the first item and goes up to the length of the tuple minus one for the last item. The index can also be negative, in which case it counts from the end of the tuple. For example, if you have a tuple t = ("a", "b", "c"), then t[0] returns "a", and t[- 1] returns "c"12
✑ Tuples can be indexed and sliced like lists, which means that you can get a single item or a sublist of a tuple by using square brackets and specifying the start and end index. For example, if you have a tuple t = ("a", "b", "c", "d", "e"),
then t[2] returns "c", and t[1:4] returns ("b", "c", "d"). Slicing does not raise any exception, even if the start or end index is out of range. It will just return an empty tuple or the closest possible sublist12
✑ Tuples can contain any data type, such as strings, numbers, booleans, lists, sets,
dictionaries, or even other tuples. Tuples can also have duplicate values, which means that the same item can appear more than once in a tuple. For example, you can have a tuple t = (1, 2, 3, 1, 2), which contains two 1s and two 2s12
✑ Tuples are written with round brackets, which means that you have to enclose the
items in a tuple with parentheses. For example, you can create a tuple t = ("a", "b", "c") by using round brackets. However, you can also create a tuple without using round brackets, by just separating the items with commas. For example, you can create the same tuple t = "a", "b", "c" by using commas. This is called tuple packing, and it allows you to assign multiple values to a single variable12
✑ The len() function can be applied to tuples, which means that you can get the
number of items in a tuple by using the len() function. For example, if you have a tuple t = ("a", "b", "c"), then len(t) returns 312
✑ An empty tuple is written as (), which means that you have to use an empty pair of
parentheses to create a tuple with no items. For example, you can create an empty tuple t = () by using empty parentheses. However, if you want to create a tuple with only one item, you have to add a comma after the item, otherwise Python will not recognize it as a tuple. For example, you can create a tuple with one item t = ("a",) by using a comma12
Therefore, the correct answers are A. Tuples are immutable, which means that their contents cannot be changed during their lifetime. and D. Tuples can be indexed and sliced like lists.
Reference: Python Tuples - W3SchoolsTuples in Python - GeeksforGeeks
DRAG DROP
Assuming that the phonc_dir dictionary contains namemumber pairs, arrange the code boxes to create a valid line of code which retrieves Martin Eden's phone number, and assigns it to the number variable.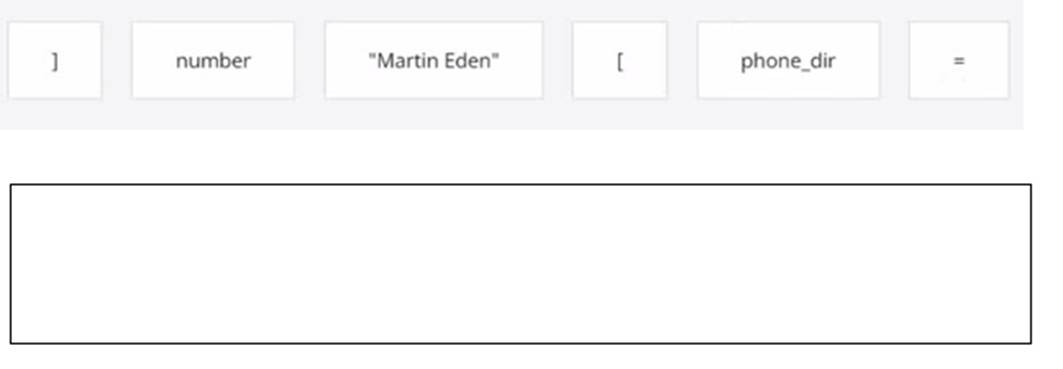
Solution:
number = phone_dir["Martin Eden"]
This code uses the square brackets notation to access the value associated with the key ??Martin Eden?? in the phone_dir dictionary. The value is then assigned to the variable number. A dictionary is a data structure that stores key-value pairs, where each key is unique and can be used to retrieve its corresponding value. You can find more information about dictionaries in Python in the following references:
✑ [Python Dictionaries - W3Schools]
✑ [Python Dictionary (With Examples) - Programiz]
✑ [5.5. Dictionaries — How to Think Like a Computer Scientist ??]
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:
A